Forklift Safety: Essential Practices to Prevent Accidents and Save Lives
August 27, 2024

Forklifts are essential tools in industries such as logistics, warehousing, manufacturing, agriculture and construction. However, despite their indispensable role, operating forklifts carries substantial safety risks. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), forklifts cause over 35,000 serious injuries and approximately 100 fatalities each year. 42% of these fatalities occur when operators are crushed by tipping vehicles.
In August 2023, a critical incident at Boston’s Logan International Airport highlighted the severe consequences of inadequate industrial truck safety measures. An employee from Oxford Airport Technical Services was operating a forklift when its forks and mast struck an entrance overhang, causing the vehicle to tip over. Tragically, the operator lost his life in the accident. OSHA’s investigation revealed that this fatality was entirely preventable, citing failures such as the lack of seat belt usage and inadequate operator training and certification.
Considering the significant risks and frequent incidents involving powered industrial trucks, this blog explores the key elements of forklift safety practices and regulatory requirements. It also examines the role of integrating advanced Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) software and artificial intelligence (AI) technology to streamline compliance and enhance safety protocols.
Forklift Safety: An Overview and Regulatory Compliance
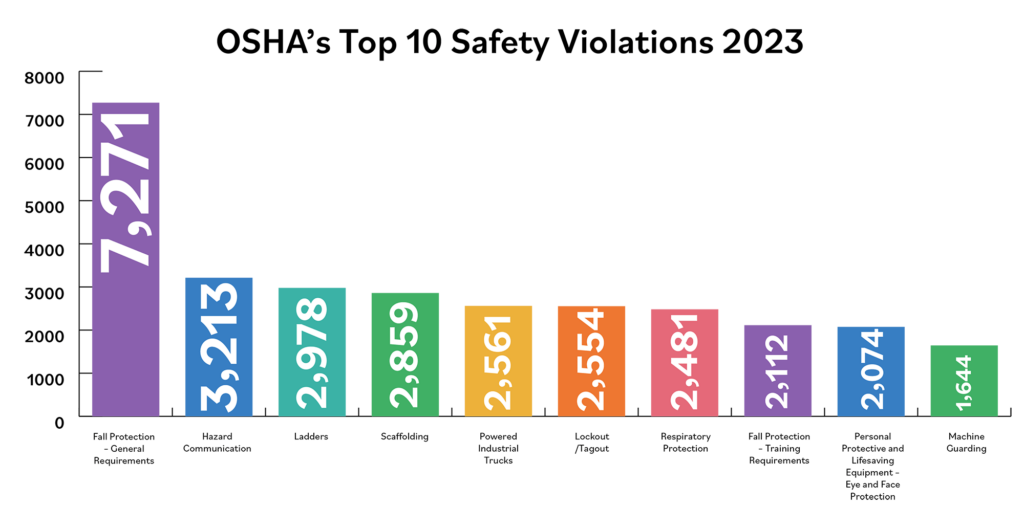
Ensuring forklift safety is essential for preventing accidents and boosting productivity in workplaces where powered industrial trucks are widely used. In 2023, industrial truck violations ranked fifth on OSHA’s Top 10 Most Frequently Cited Standards list, with 2,561 recorded instances. Among those, the three leading causes of fatalities were overturns, collisions with workers on foot and falls from forklifts.
Implementing forklift safety involves practices and procedures designed to prevent accidents and injuries. This includes proper training, regular maintenance, use of safety equipment and adherence to regulatory guidelines. In the U.S., OSHA’s standards (29 CFR 1910.178) outline requirements for operator training, equipment maintenance and workplace layout to mitigate risks. In the European Union, the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC provides comprehensive guidelines on the use of powered industrial trucks. Similarly, both Canada’s Occupational Health and Safety Regulations and the United Kingdom’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE) mandate that employers provide proper training and ensure regular inspections and maintenance of forklifts to prevent workplace accidents.
Prominent cases highlight the importance of safeguarding measures to protect workers and the significant financial penalties organizations face when they neglect forklift safety. For instance, a manufacturing plant in Ohio was fined $190,000 after a forklift accident resulted in a worker’s leg amputation due to lack of proper training and maintenance. In another case, a depot in Newark, UK, was fined £500,000 after a forklift truck overturned, resulting in the operator’s death. Beyond the financial consequences, such common accidents typically lead to significant disruptions, including temporary shutdowns for investigations, retraining of staff, implementation of new safety protocols and delays in production and logistics.
Key Elements of Forklift Safety
Ensuring comprehensive forklift safety involves several key components that help organizations meet regulations, protect workers and maintain operational efficiency. These include:
Addressing Common Hazards
Safety protocols for forklift operations must address various common hazards, including:
- Blind spots that can hide pedestrians or obstacles, increasing the risk of collisions.
- Unstable and suspended loads that can shift or fall, leading to accidents and injuries.
- Pedestrian traffic in areas where forklifts operate can lead to serious accidents. In fact, OSHA statistics reveal that 36% of forklift fatalities involve a pedestrian.
- Improper load handling, which can cause the forklift to become unbalanced and tip over.
- Insufficient lighting in the work area, making it difficult for operators to see obstacles or pedestrians.
- Congested work areas, which can limit maneuverability and increase the likelihood of collisions.
- Weather conditions such as wet or icy surfaces that can reduce traction and control.
- Personnel riding on forks as forklifts are not designed to lift people.
Addressing these hazards through proper training, clear signage and safe operational practices can significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Proper training is the cornerstone of forklift safety. OSHA mandates thorough training and certification for all forklift operators, encompassing operational skills, safety protocols, hazard awareness and emergency procedures. Employers must develop a training program based on safe truck operation principles, the types of vehicles used, the specific workplace hazards and OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.178 standard.
Effective training programs reduce the risk of accidents by ensuring operators are well-informed about safe practices and regulations through formal and practical instruction. Training must cover both truck-related topics, such as operating instructions, warnings and precautions, and workplace-related topics, including surface conditions, load stability and pedestrian traffic. Employers must provide refresher training when operators demonstrate deficiencies, are involved in incidents, are assigned different trucks or when workplace conditions change. Organizations must also certify and evaluate each operator at least once every three years to ensure ongoing competence.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Preventing mechanical failures that can lead to accidents relies heavily on regular maintenance and inspections. Daily forklift inspections should include checks on brakes, steering, warning devices and tires. Industry-specific problems, such as corrosive material exposure in chemical plants and debris accumulation in construction sites, also require attention to maintain safe operations. Consequently, organizations must schedule periodic inspections and maintenance to address potential issues before they become serious hazards, which ensures safe operation and extends the equipment’s lifespan.
Guidelines for Safe Forklift Operation
Safe forklift operation depends on several best practices. Main guidelines are:
- Ensuring all operators are properly trained and certified.
- Conducting regular maintenance and removing from service any forklift in unsafe operating condition.
- Following proper load handling procedures, ensuring loads are secure, balanced and within the rated capacity to prevent tipping.
- Adhering to speed limits and operating within designated areas to avoid collisions.
- Using seat belts and other safety devices at all times.
- Keeping the load low to the ground when moving to maintain stability.
- Avoiding sharp turns and sudden stops to prevent accidents.
- Keeping a safe distance from platform and ramp edges.
- Maintaining clear visibility of the work area and ensuring enough clearance when raising, loading and operating the forklift.
- Ensuring that no one walks or stands under a suspended load to prevent serious injuries from falling objects.
- Being aware of other vehicles and pedestrians in the work area and using horns at cross aisles and obstructed areas.
- Observing the “No riders” rule and never using the forks to lift people.
Figure 1: 12 Best Practices for Safe Forklift Operation

Designing a Safe Workplace Layout
A well-designed workplace layout can significantly enhance forklift safety and minimize the risk of accidents. Important considerations include creating clear pathways for forklifts that are unobstructed and well-defined to ensure smooth and safe movement. It is also essential to segregate pedestrian traffic from forklift operating areas to reduce the risk of collisions, which is a common cause of injuries. Adequate space for forklifts to maneuver safely is necessary, as crowded areas increase the risk of accidents. Placing racking and storage systems strategically to minimize forklift travel distances additionally reduces the likelihood of accidents during transit. These design elements not only prevent collisions and other accidents but also contribute to a more organized and efficient workflow.
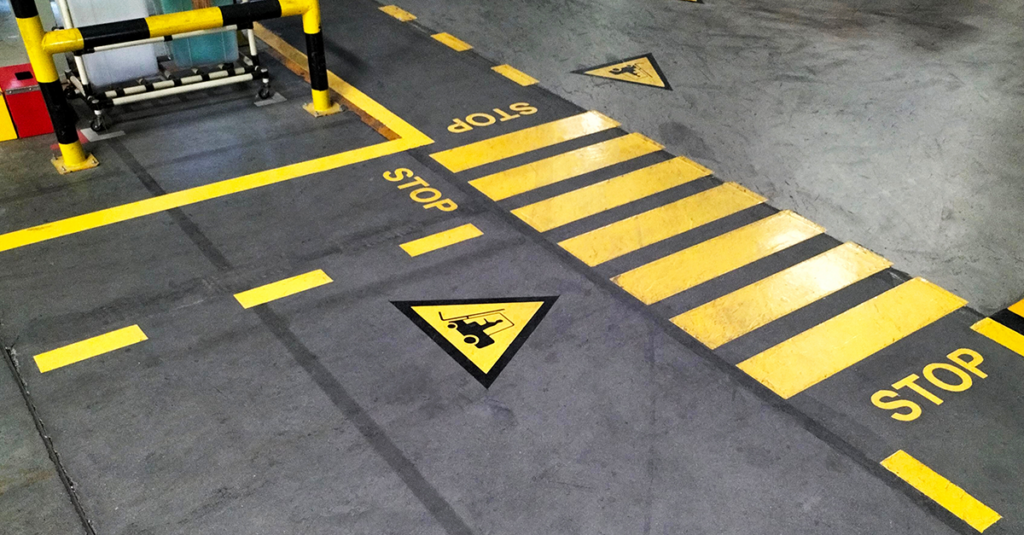
Signage and Marking for Forklift Paths
Proper signage and floor markings guide forklifts effectively and help maintain operator and pedestrian safety. Clearly marked paths for forklifts direct traffic and prevent interference with other activities. Warning signs for pedestrians should alert them to forklift operations and designate safe walking areas to avoid accidents. Directional and instructional signs provide operators with clear instructions on travel direction, loading and unloading zones and any potential hazards in the area. All signs and markings should be visible under all lighting conditions and comply with OSHA and other relevant safety standards, indicating safe operating speeds, load limits and pedestrian crossings.
Figure 2: Clearly Defined Traffic Zones in an Industrial Building

The Role of EHS Software in Enhancing Forklift Safety
Intelex offers a comprehensive suite of advanced Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) software to support industrial truck safety. These solutions streamline and enhance critical safety management functions, making the workplace more secure and efficient. Key benefits include:
- Ensuring up-to-date training for all operators: Intelex’s Training Management Software tracks training schedules and certifications to ensure forklift operators are properly trained and compliant with current safety standards.
- Scheduling and documenting regular maintenance and inspections: Intelex’s Job Safety Analysis Software automates routine maintenance and inspections for forklifts, ensuring thorough checks and comprehensive maintenance records.
- Real-time tracking of maintenance issues and resolutions: EHS software monitors and resolves maintenance issues immediately, enabling safety managers to quickly address potential threats.
- Streamlining incident reporting processes: Intelex’s Incident Reporting Software simplifies documentation and reporting of safety incidents for timely responses and root cause analysis.
- Analyzing data to identify patterns and prevent future incidents: EHS software uses data analytics to detect patterns and trends in safety incidents, identifying common issues and implementing preventative measures to avoid future accidents.
- Maintaining regulatory compliance: Intelex’s Compliance Tracking Software helps organizations stay compliant with OSHA regulations and industry standards by tracking regulatory changes and ensuring all safety practices meet required guidelines.
- Generating compliance reports: EHS software facilitates the generation of compliance reports for audits, ensuring transparency and accountability in safety practices.
AI Advancements and Forklift Safety
Supplementing EHS software solutions, AI enhances forklift safety through sophisticated monitoring and predictive capabilities. Protex AI, in collaboration with Intelex, leverages real-time data to detect unsafe practices and potential hazards. AI-powered cameras and sensors continuously monitor forklift activities, identifying risky behaviors such as speeding and improper load handling. When the system detects hazards, it promptly alerts operators and safety managers, enabling immediate corrective actions and reducing the risk of accidents.
In addition to real-time monitoring, Protex AI uses predictive analytics to analyze data and identify unsafe patterns. This proactive approach allows organizations to address potential hazards before they result in accidents and injuries. Integrating Protex AI with Intelex’s EHS software streamlines data collection, safety reporting and compliance tracking, ensuring consistent observation of regulatory standards. This combination also enhances training programs by providing data-driven insights into operator performance, creating a safer and more efficient workplace environment.
Moving Forward with Enhanced Safety
In industries where forklifts are commonly used, including retail, warehousing, manufacturing and construction, organizations must prioritize forklift safety to prevent accidents and protect workers. This involves taking a comprehensive approach that addresses common hazards, provides thorough training and ensures regular maintenance.
By designing safe workplace layouts and integrating advanced EHS software, employers can streamline training, maintenance, incident reporting and regulatory compliance. AI-driven solutions can further improve safety with real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, enabling more proactive risk management.
When enterprises adopt such strategies and innovations, they can significantly reduce forklift-related accidents and promote a safety-first culture. This commitment to continuously improving and actively managing safety creates a safer and more productive work environment that benefits both workers and the organization.






