How to Build User Adoption into Your EHS Software Rollout
August 27, 2025
7 minute read

“How do you build user adoption and engagement with the new system?” This question, asked by a customer during a recent consultation call, cuts to the heart of one of the most persistent challenges facing EHS professionals today.
Technology is just a tool. Without genuine engagement from users across all levels of the organization, even the most sophisticated EHS platform will collect digital dust.
Driving engagement extends far beyond the initial rollout phase.
It requires a strategic, phased approach that addresses both the immediate concerns of implementation and the long-term sustainability of the system. It must account for the diverse needs of different user groups, from frontline workers who input data daily to executives who use the data to guide critical decisions.
Understanding the engagement challenge
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to understand why EHS technology engagement often fails.
| Barrier | Cause |
|---|---|
| Resistance to Change | Frontline workers, supervisors, and even management teams often view new technology as an additional burden rather than a helpful tool. This perception is frequently rooted in past experiences with poorly implemented systems or inadequate training. |
| Lack of Clear Value Proposition | When users don’t understand how the technology will benefit them personally or improve their work processes, engagement naturally suffers. The “what’s in it for me” question must be answered convincingly for each user group. |
| Inadequate Training and Support | Many organizations focus heavily on the technical aspects of training — how to navigate screens and complete forms — while neglecting the equally important “why” behind these actions. |
| Disconnected Data and Feedback Loops | When users input data but never see how it’s being used or what improvements result from their efforts, they quickly lose motivation to maintain high-quality engagement. |
Short-term strategies to build a strong foundation for engagement
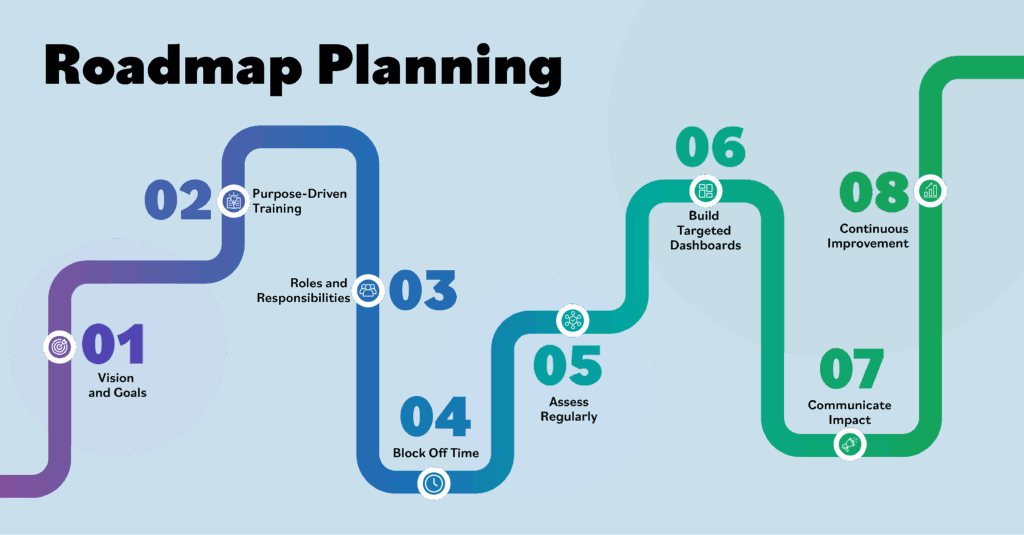
1. Establish a clear mission and vision
The foundation of any successful EHS technology initiative must be a clearly articulated mission and vision that resonates across all organizational levels. This step is frequently overlooked in favor of rushing into technical implementation, but it’s arguably the most critical component of long-term success.
Establishing a clear mission and vision for the initiative helps ensure that the purpose and intended outcomes are accurately communicated from the frontline to the executive teams.
Read The EHS Goal Setting Guide to learn how to write your vision and mission.
2. Train on the “why” not just the “how”
Traditional EHS technology training focuses heavily on the mechanical aspects of system use — which buttons to click, which fields to complete, and how to navigate between screens. While this technical training is necessary, it’s insufficient for driving meaningful engagement.
Effective training programs must address three critical “why” components.
| Why the information matters | Users need to understand how the data they’re collecting contributes to broader safety objectives. For instance, when training workers on incident reporting, explain how their detailed observations help identify trends that prevent future incidents, protect their colleagues, and improve overall workplace conditions. |
| Why their input is vital | Each user group must understand their unique role in the broader EHS ecosystem. Frontline workers should know that their observations and near-miss reports are often the first indicators of potential hazards. Supervisors need to understand how their timely review and response to reports maintains momentum and demonstrates organizational commitment to safety. |
| Why it benefits them personally | This is perhaps the most important component. Users need to see clear, personal benefits from their engagement with the technology. These benefits might include easier access to safety information, streamlined reporting processes, or enhanced ability to identify and address workplace hazards that could affect them directly. |
3. Define clear roles and responsibilities
Role ambiguity is a significant source of stress and disengagement during technology implementations. When people don’t understand exactly what’s expected of them, they often default to minimal compliance or, worse, they become overwhelmed and disengaged.
Successful EHS technology implementations include detailed role definitions for each user persona in the organization:
- Frontline workers: Clearly define what they should report and what level of detail is expected. Provide specific examples of high-quality submissions and explain how their contributions fit into the larger safety picture.
- Supervisors: Outline their responsibilities for reviewing, responding to, and acting on worker submissions. Establish clear time frames for these activities and provide guidance on appropriate responses to different types of reports.
- EHS professionals: Define their role in analyzing data, identifying trends, and developing action plans based on the information collected through the system.
- Leadership: Establish expectations for their involvement in reviewing dashboards, participating in safety discussions based on system data, and demonstrating ongoing commitment to the initiative.
4. Allocate adequate time for engagement
One of the most common mistakes in EHS technology implementation is asking for increased engagement without providing additional time for these activities.
This approach sends a conflicting message: while organizations claim the initiative is important, they’re unwilling to adjust schedules or processes to accommodate it.
Successful implementations work with operations teams to identify opportunities for integrating EHS technology use into existing workflows or, when necessary, making small adjustments to schedules to accommodate new requirements. This might involve:
- Building safety observation time into daily work schedules
- Incorporating system use into existing safety meetings or toolbox talks
- Providing dedicated time during pre-start meetings or shift changes for hazard ID or workplace inspections
When organizations make these time investments, it signals that the EHS technology initiative is a genuine priority rather than a “flavor of the month” exercise.
Long-term strategies for sustaining and improving engagement
5. Continuous assessment and optimization
The most successful EHS technology implementations treat engagement as an ongoing process rather than a one-time achievement. This requires regular assessment of what information is being collected, how it’s being used, and whether it continues to provide value to users and the organization.
Periodic data quality analysis should be conducted to identify:
- Fields or forms with consistently poor completion rates
- Information that’s being collected but rarely used in decision-making
- User feedback about system complexity or unnecessary requirements
- Opportunities to streamline processes based on actual usage patterns
It’s always easier to add complexity to a system than to remove it, but regular pruning of unnecessary elements is essential for maintaining user engagement.
6. Build targeted dashboards and metrics
Different user groups need different information presented in different ways. A dashboard that works well for executive leadership will likely be overwhelming or irrelevant for frontline workers, and vice versa.
Effective dashboard design follows the principle of “right information, right person, right time”:
- Frontline worker dashboards: Focus on information that directly impacts their daily work. I.e., recent hazards in their area, upcoming training requirements, or safety performance metrics for their immediate team/site/department.
- Supervisor dashboards: Emphasize actionable items requiring their attention. I.e., pending investigations, team performance metrics, and trends that might require intervention.
- Management dashboards: Provide strategic oversight information. I.e., organizational performance trends, compliance status, and goals/objective attainment.
- Executive dashboards: Focus on high-level performance indicators, regulatory compliance status, and strategic safety metrics tied to business objectives.
Getting the right level of information to the right people at the right time will ensure the data that is collected in the EHS technology tool is relevant and actionable for the organization.
7. Communicate impact and drive continuous improvement
Perhaps the most critical long-term engagement strategy is demonstrating how user input drives real improvements. When workers see that their safety observations lead to hazard corrections, their incident reports result in process improvements, or their suggestions are implemented, engagement naturally increases.
Effective communication strategies include:
- Regular success stories. Share specific examples of how worker input through the EHS system led to meaningful safety improvements. These stories should be specific, credible, and relatable to the audience.
- Trend analysis communication: Help users understand how their individual contributions fit into larger patterns and trends. For example, show how multiple near-miss reports from different workers revealed a systemic issue that was then addressed.
- Closed-loop feedback: Ensure that every significant submission receives appropriate follow-up communication. Users should know that their input was received, reviewed, and when appropriate, acted upon.
- Performance recognition: Acknowledge individuals and teams who demonstrate exceptional engagement with the EHS technology system but be careful to focus on quality of engagement rather than just quantity of submissions.
See how this Australian-based energy company achieved incredible results partnering with Intelex as part of their Live Work Better initiative.
Intelex platform features that support engagement
Intelex’s platform incorporates specific features designed to reduce friction and increase user engagement.
These technical features can help enable a comprehensive engagement strategy.
| Intelex feature | How it increases user engagement |
|---|---|
| QR code integration | Allows users to quickly access relevant forms or information by scanning codes posted in work areas or attached to their worker ID badge, eliminating the need to navigate through menu structures. When QR codes are scanned then can prepopulated designated fields to make sure that standardized information like location or equipment are pre-selected. |
| Responsive web interface | Ensures that the system works equally well on desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones, allowing users to engage with the platform using their preferred device, even if they do not download a native mobile application. |
| Offline capability | Enables data collection in areas with poor network connectivity, ensuring that users can complete their safety-related tasks regardless of technical limitations. |
| Mobile-first design | Recognizes that many frontline workers are more comfortable with mobile interfaces than traditional desktop applications. Allowing workers to engage with the Intelex system while in the field is critical to boosting engagement. |
Measuring success and adjusting strategy
Successful EHS technology engagement requires ongoing measurement and adjustment. Key performance indicators should include both quantitative and qualitative metrics:
Quantitative metrics:
- User login frequency and session duration
- Form completion rates across different user groups
- Data quality scores based on completeness and accuracy
Qualitative metrics:
- User satisfaction surveys focusing on system utility and ease of use
- Focus group feedback from different user personas
- Anecdotal feedback from supervisors about worker engagement levels
- Assessment of data quality and actionability by EHS professionals
Conclusion
Driving engagement with EHS technology systems requires a strategic, multi-phased approach that addresses both technical and human factors.
A successful implementation goes far beyond technical deployment. It encompasses change management, communication, training, and ongoing optimization.
Want to see how you can meet your safety, quality, and sustainability goals with Intelex in two easy steps? Visit our Custom EHSQ Demo Tour.







